Streamlit and Pygwalker: Simplify Data Visualization and Exploration
Welcome to an exciting journey where we explore the amazing capabilities of Streamlit and Pygwalker in analyzing and visualizing data effortlessly. Get ready to immerse yourself in the world of interactive data exploration!
Introducing Streamlit
Streamlit is a powerful Python library that simplifies the process of transforming your data scripts into interactive web applications. With Streamlit, you can bid farewell to the complexities of web development and coding challenges. It's a fast, open-source, and free solution for building and sharing data applications.
Exploring Data Made Easy with Pygwalker
Pygwalker, on the other hand, is a popular Python library designed specifically for data analysis and visualization. It provides data scientists and analysts with an intuitive interface for generating captivating visualizations, including scatter plots, line plots, bar charts, and histograms. The best part? You don't need any coding skills to use Pygwalker!
To learn more about Pygwalker and access additional examples and resources, visit the official Pygwalker GitHub Page.
Getting Started with Streamlit and Pygwalker
Before we embark on our data exploration journey, let's make sure your computer is equipped with a Python environment (version 3.6 or higher). Once you have that set up, follow these steps:
Installing the Required Dependencies
Open your command prompt or terminal and run the following commands to install the necessary dependencies:
```shell
pip install pandas
pip install pygwalker
pip install streamlit
```
Incorporating Pygwalker in a Streamlit Application
Now that we have all the dependencies installed, let's create a Streamlit application that incorporates Pygwalker. Create a new Python script called `pygwalker_demo.py` and add the following code:
```python
import pygwalker as pyg
import pandas as pd
import streamlit.components.v1 as components
import streamlit as st
# Configure the Streamlit page
st.set_page_config(
page_title="Using Pygwalker with Streamlit",
layout="wide"
)
# Add a title
st.title("Using Pygwalker with Streamlit")
# Import your data
df = pd.read_csv("https://sample.csv")
# Generate the HTML using Pygwalker
pyg_html = pyg.walk(df, return_html=True)
# Embed the generated HTML into the Streamlit app
components.html(pyg_html, height=1000, scrolling=True)
```
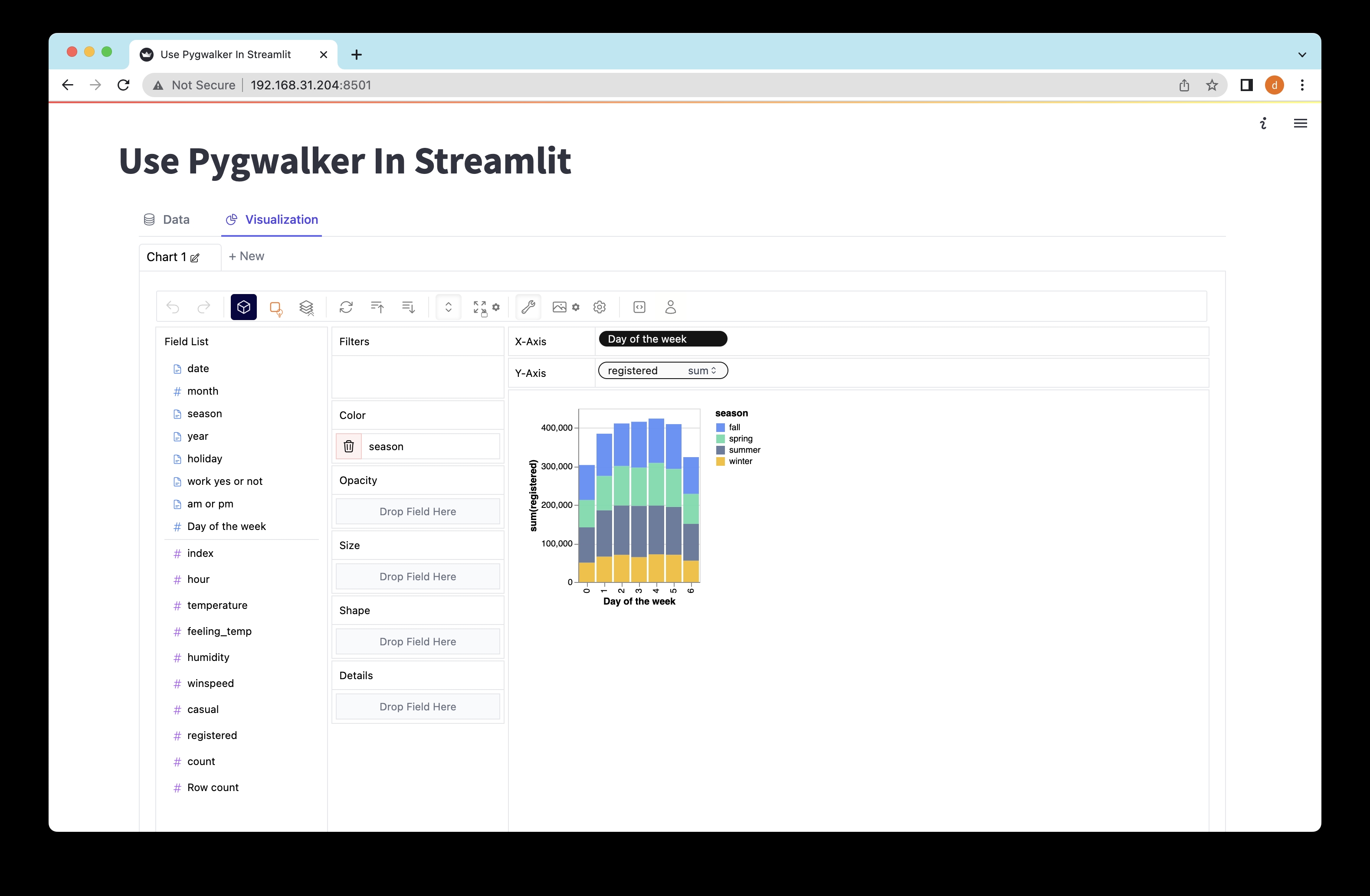
Exploring Data with Pygwalker in Streamlit
To launch the Streamlit application and start exploring your data, run the following command in your command prompt or terminal:
```shell
streamlit run pygwalker_demo.py
```
You will see some information displayed on the terminal. Access the Streamlit app in your browser using the provided URL:
Local URL: [http://localhost:8501](http://localhost:8501)
Network URL: [http://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:8501](http://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:8501)
Open the provided URL ([http://localhost:8501](http://localhost:8501)) in your web browser and witness the power of Pygwalker's intuitive drag-and-drop actions for interactive data exploration and visualization.
Saving the State of a Pygwalker Chart
If you want to save the state of a Pygwalker chart, follow these simple steps:
1. Click the export button on the chart.
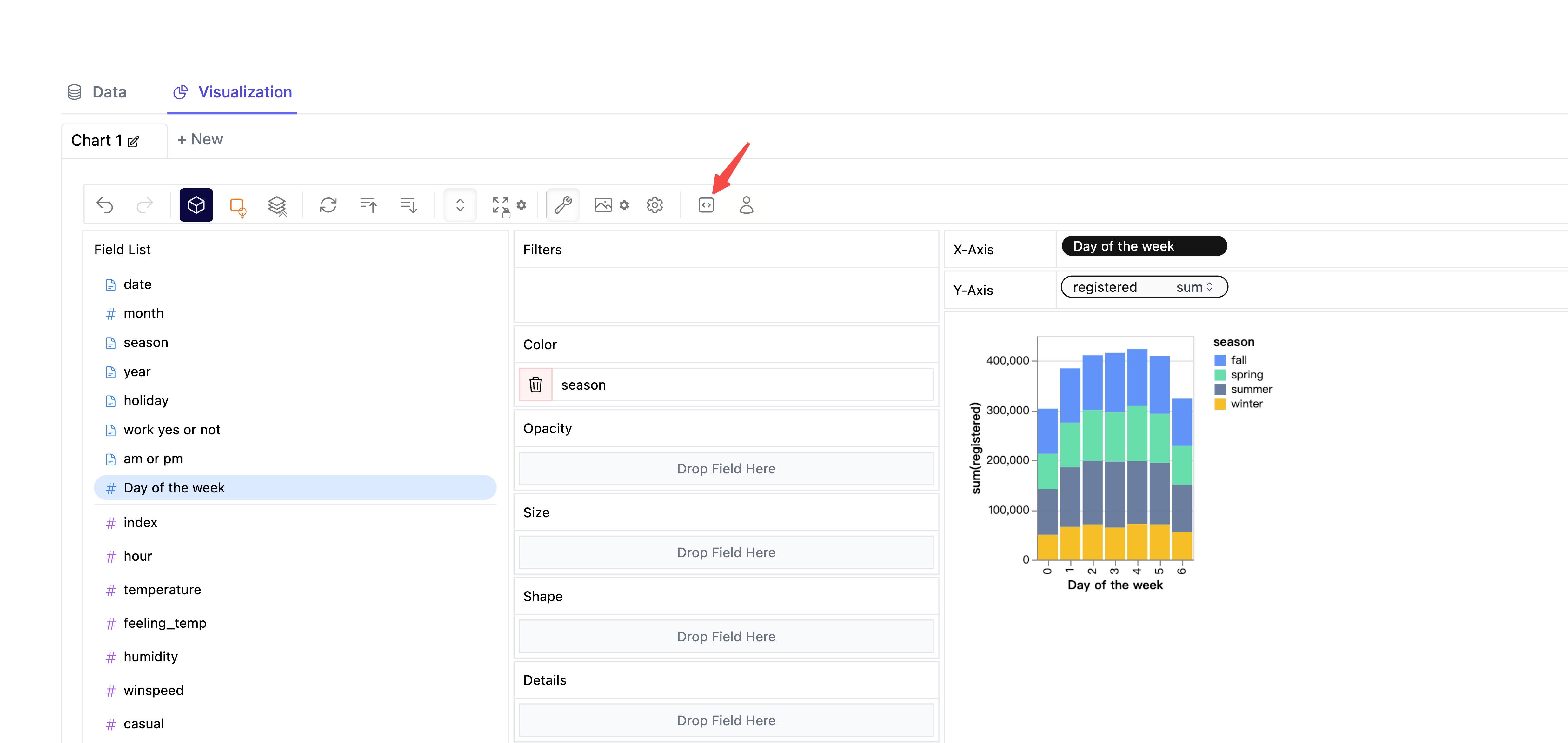
2. Click the copy code button.
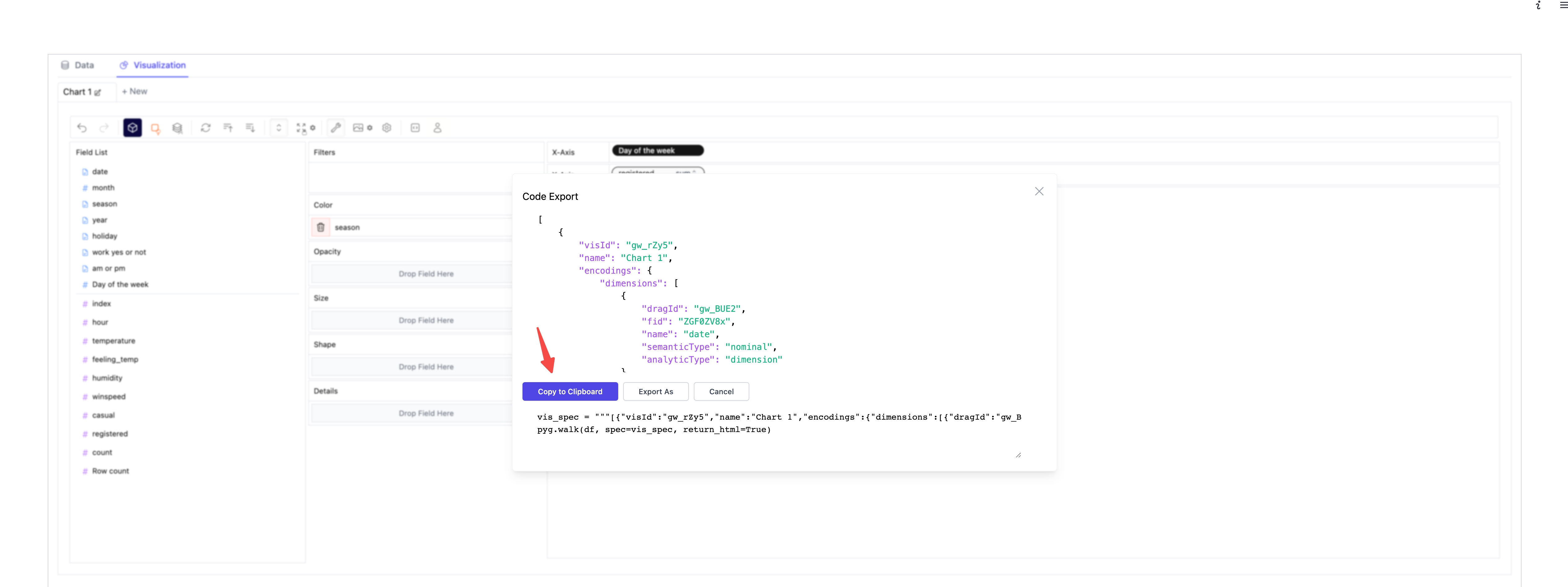
3. Paste the copied code into your Python script where needed.
```python
import pygwalker as pyg
import pandas as pd
import streamlit.components.v1 as components
import streamlit as st
# Configure the Streamlit page
st.set_page_config(
page_title="Using Pygwalker with Streamlit",
layout="wide"
)
# Add a title
st.title("Using Pygwalker with Streamlit")
# Import your data
df = pd.read_csv("https://kanaries-app.s3.ap-northeast-1.amazonaws.com/public-datasets/bike_sharing_dc.csv")
# Paste the copied Pygwalker chart code here
vis_spec = """<PASTE_COPIED_CODE_HERE>"""
# Generate the HTML using Pygwalker
pyg_html = pyg.walk(df, spec=vis_spec, return_html=True)
# Embed the generated HTML into the Streamlit app
components.html(pyg_html, height=1000, scrolling=True)
```
Make sure to refresh the webpage to see the saved state of your Pygwalker chart.
It's important to note that Pygwalker is built upon graphic-walker, a powerful library that can be embedded in various platforms, including Excel and Airtable. This means that your Pygwalker app can easily collaborate with users in different environments, leveraging the capabilities of graphic-walker and Pygwalker.
Conclusion
Streamlit and Pygwalker are invaluable tools that simplify data exploration and facilitate effective communication of insights. Streamlit's user-friendly interface and Pygwalker's interactive visualization options seamlessly enhance your data analysis workflow. So go ahead, dive into your data, and share your remarkable insights with the world!
References
For more detailed information, you can refer to this documentation that explains how to use Streamlit with PyGWalker.
Comments
Post a Comment